A Day in Operations:
“Christine, why is the Sales Order showing a different price than the Customer’s PO?”
“Mark, why is the pallet that heavy? The invoice shows a lower weight!”
“Carol, could you explain, why the goods are not yet loaded?”
“Tom, when will the goods finally arrive?”
Do these questions sound familiar to you? If so, then let’s discuss a topic, which isn’t very sexy, but is a key contributor to the success of an organization’s operations: Master data.
1. What is Master data?
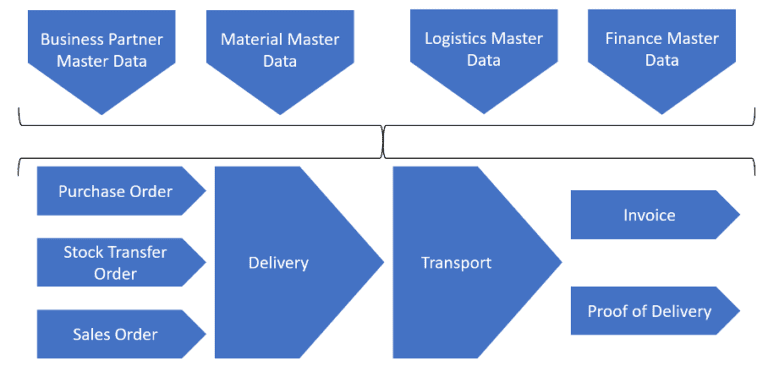
Master data is the backbone of all operations. It provides critical information about relevant objects in a specific process. Based on Master data, Movement data (e.g., Sales/Purchase Orders, Material Movement Records) is generated within the process.
Creating and maintaining Master data is normally decoupled from the daily operations of a company.
Master data has different categories and their validity periods may differ – some expire within short notice (e.g. special discounts), some are valid for unlimited time (e.g. material number, plant address). Some are evident, some work hidden in the background.
a) Customization Settings
This type of Master data is normally stored within the relevant IT system’s customization and sets the playing fieldof the according process. This is the most difficult part of the master data because only its impact on the transaction data is visible – and it is quite difficult to trace the problem back to a specific setting.
Accordingly, this area carries the highest risk of disappointment in an organization and, consequently, of manual bypassing of the system in question.
b) Master data
This is the best-known type of Master data, which including amongst others: material, business partners (suppliers, customers other parties), purchasing information records and sales conditions. Sources for this type of Master data include internal information (e.g., material resource planning scheme), external information (e.g., purchasing price and currency), and a combination of both (e.g. lead-time of a product, depending on the fact, whether it is sourced internally or externally).
2. What Makes Master Data Make So Important?
For any process within an ERP-System, Master data provides…
a) …relevant input to processes AND
b) …key elements to steer processes in the right direction.
Thus, correct Master data is crucial to achieve the desired output.
In other words:
A company, which has full control of its Master data, its accuracy and precision, will face significantly less issues in its da
ily operations and, thus, will save a lot of precious resources. And that’s a huge competitive advantage!
3. Challenges
Master data management faces many challenges, amongst them:
a) Understanding the importance of clean Master data – most people do not realize, where the pain in their daily work really comes from. Popular excuses are: “the system doesn’t work as foreseen.” The important question, however, is: why does the ERP-system work the way it does and not the way it meant to? Most frequently, Master data is the key to solving this issue.
b) Identify relevant Master data – this is a huge problem, as many Process Owners are unable to clearly break down, which Master data is a relevant input to their processes and what is required to steer these processes. This is a great opportunity for Business Process Consulting Department and makes this function a key element in any company.
c) Completeness and Accuracy – plenty Master data templates include fake values, simply for the purposes of “completeness”; but then, nobody updates those values anymore. Accordingly, data completeness and accuracy are essential.
d) Flexibility & Complexity of Data Structures – SAP faced an issue, which resulted in a major change from R/3 to S/4: in R/3, the Supplier and Customer Master data were strictly separated. But what about subcontractors, who are both customer (receiving the semi-finished goods) and supplier (shipping the finished goods)? SAP S/4 HANA has a new section, which is called “Business Partner Master data”. With this approach, SAP offers its customers greater flexibility in setting up their partners. Many companies face the same rigid conflict in their Master data-setup: for specific reasons, a highly complex model, reflecting all and every exception and detail, has evolved over years, sometimes decades. But when a new category needs to be added to the Master data, the setup collapses due to its inflexibility. With this being one of the biggest risks in Master Data, accordingly, Master Data Management needs to protect Master data from rigidity and over-complexity.
e) Do not accept fake values – to finalize the setup process, it is very common to use “placeholder values” for certain forms for e.g. new materials, customers, suppliers, routes. Oftentimes, the intention behind this, is to replace these fake values with true values lateron. Let me summarize it this way: they will NEVER EVER be updated. So, please ensure correct data right from the beginning, as cleanup sessions are by far more painful afterwards, because you need to…
- …identify the affected items and
- correct them.
f) Update Cycles – you think, the weight of a product will never change? Continuous improvement, design changes, components from different suppliers etc. may have an impact on the net and gross weight of a product. Thus, it should be a joint effort for the various stakeholders to agree on regular update cycles – as well as on updates outside the regular cycle, whenever needed. Ideally, this is embedded in the Product Lifecycle Management.
g) Interdependencies – the biggest challenge is to fully understand the interdependencies between various Master data and the impact of these combinations on the process output. Sound knowledge of the ERP-programs and the single process steps is required to avoid negative surprises.
4. Solution path
There is no single, fits-all solution, but the following points can help guide organizations:
- Top Management commitment: even if Master Data Management is not yet its own type of Management System (like Quality, EHS etc. are), top management commitment is required to have the buy-in from all necessary resources, tasks, efforts. Furthermore, top management should also provide the overall framework for Master Data Management and highlight the importance of accurate and complete data to the whole organization.
- Clear roles & responsibilities: it is not only about ownership of the process. Even more important are the responsibility and accountability for continuous reviews and updates to the Master data.
- Small buckets: even if a full end-to-end understanding of processes is required, it makes a lot of sense to slice the processes down into smaller buckets, which are analyzed for Master data requirements.
Hint: start from the end! In this way, you can determine where the master data is needed and where it must be available at the latest.
- Competences and Resources: 2-3 Teams play an important role in solving the topic:
- Business Process Owners
- Master Data Management (if not done by Business Process Owners)
- Business Process Consultancy
All of them need to be capable of overlooking the process end-to-end; it definitely helps, if Master Data Management and Business Process Consultancy have a sound understanding of stakeholders’ (especially legal) requirements for consideration within the process.
- Stakeholders: the identification of ALL relevant stakeholders requires a good overview of the process itself and all its implications – in any direction! This is challenging, but when successfully implemented, you should have a complete overview of data required at a certain process step.
- Checks, Controls & Metrics: as part of a governance model, continuous reviews of the existing data for inconsistencies, incompleteness, modification requirement should be regularly implemented. Based on the outcome of the relevant metrics, improvement and update projects can be defined.
Summarizing the topic, Master data require – at any time of its lifecycle – the full attention of the organization to ensure that…
- …processes are setup correctly and completely.
- …inputs provided are processed as expected and achieving the desired output.
- …all relevant controls and compliance checks are executed properly.
To achieve this goal, organizations require top management commitment for data excellence and accordingly, highly competent people in Business Consultancy (acting as intermediate between operations and IT) and in Master Data Management, who have a global understanding of the processes in use, their interdependencies, complexity.